 |
 |
 |
| Home | More Articles | Join as a Member! | Post Your Job - Free! | All Translation Agencies |
|
|||||||
|
|
Translation Quality Management Model for Multilanguage localization in Outsourcing Environment
TQM is the quality management practice which utilizes PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Action) principle. Meanwhile, TQM provides some organizations with the methods to set up the translation quality management system. Intel Globalization & Localization (GLS) China team is a new service provider for internal localization & globalization requirements. It manages multi-language localization by outsourcing. GLS China adopts the TQM model to enhance its translation quality management system since it was established. This article is a summary of its practice in managing localization quality. 1. Overview Localization is an important requirement in many international corporations. It is utilized in many kinds of services, such as translation, QA, DTP, testing, and project management. The localization organization needs provide localization solution for multiple languages. Most corporations centralize the localization service by using outsourcing. Localization organizations might meet some common challenges with translation quality management in today’s complicated outsourcing environment such as:
It is important to build a translation quality management system to manage multiple-language localization. Only with effective quality management, can the localization project manager be confident of the quality delivered. 2. TQM Model Architecture The purpose of the TQM Model is to keep the translation quality on the track of continuous improvement. It is a basic structure of translation quality management system. Localization specialists can use mature existed knowledge or technology to enrich the quality management system. Take ISO9001 as an example, it is nowadays utilized in many organizations to manage quality. Some important principles are quite useful to manage translation quality. Meanwhile the localization organization can improve the quality system through self-development.
3. Standard Set There are two kinds of standards in Standard set: Translation Standard and Evaluation Standard. Translation standard Translation standard is the collection of all translation requirements. The organization needs to document its translation standard and made it available to all involved vendors as well as internal project managers. For an international company, the translation standard consists of three levels of standards according to applicable scope.
The translation standard can be gradually developed from many sources. Such as: External
Internal
For a new localization organization, LISA QA Model can be the reference to quickly establish the translation standards. Localization specialist can get some idea from LISA QA Model to establish a general translation standard. As for local language translation standard or corporation translation guide, it needs to be developed gradually. Evaluation standard Evaluation standard is the criteria to measure the quality of translation. It is the document that usually defines the following items:
The evaluation standard is to help the localization organization get measurable data on translation quality. It is important for organizations to define quality objective, conduct analysis and corrective action. 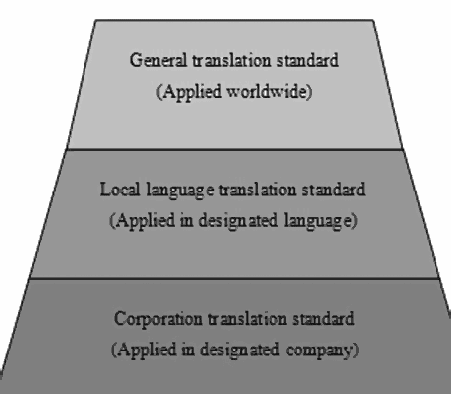
4. Process Set The localization organization can develop its processes to make quality management systems more effective depending on the actual situation. The processes usually cover the following areas:
Among the above processes, the Quality evaluation process is the primary process. For a new localization organization, it can outsource linguistic QA work to a qualified vendor. The QA vendor needs to take independent work and provide a qualified QA report. The chart below is an example of the Quality evaluation process. Other processes are secondary processes. They can lubricate the engine of the translation quality management system. For an example of the terminology management process, it is helpful to enhance the terminology consistency so as to iprove the quality. In the outsourcing environment, when many vendors are used for the business, terminology consistency will become a serious problem. An Organization can develop processes depending on the real situation. The TQM model will be enriched as more and more processes are developed. A repository can be set up to keep the output of the processes for future review.
5. Interaction of translation quality management model PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Action) is an important principle in quality management. According to PDCA principle, the interaction of TQM model can consists of 4 circular stages. a. Plan translation quality management system
b. Execute TQM System
c. Measure, Review and analyze Quality Management Performance
d. Review and Analyze Quality Management System and obtain follow- up action
6. Summary TQM is not an abstract theory. It is the
summary from practice. It does help new localization organizations
build up translation quality management systems and improve
localization quality continuously. ClientSide
News Magazine - www.clientsidenews.com
E-mail this article to your colleague! Need more translation jobs? Click here! Translation agencies are welcome to register here - Free! Freelance translators are welcome to register here - Free! |
|
|
Legal Disclaimer Site Map |