Mathematical jargon glossary
By
Wikipedia,
the free encyclopedia,
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_jargon
Become a member of TranslationDirectory.com at just
$12 per month (paid per year)
Advertisements:
Use the search bar to look for terms in all glossaries, dictionaries, articles and other resources simultaneously
The language of mathematics has a vast vocabulary of specialist and technical terms. It also has a certain amount of jargon: commonly used phrases which are part of the culture of mathematics, rather than of the subject. Jargon often appears in lectures, and sometimes in print, as informal shorthand for more rigorous arguments or more precise ideas. Much of this is common English, used in a mathematical or quasi-mathematical sense.
Note that some phrases, like "in general", appear in more than one section.
Philosophy of mathematics
These terms discuss mathematics as mathematicians think of it; they connote common intellectual strategies or notions the investigation of which somehow underlies much of mathematics.
abstract nonsense
Also general abstract nonsense or generalized abstract nonsense, a tongue-in-cheek reference to category theory, using which one can employ arguments that establish a (possibly concrete) result without reference to any specifics of the present problem.
canonical
A reference to a standard or choice-free presentation of some mathematical object. The term canonical is also used more informally, meaning roughly "standard" or "classic". For example, one might say that Euclid's proof is the "canonical proof" of the infinitude of primes; indeed, this is a canonical example of a canonical proof.
elegant
Also beautiful; an aesthetic term referring to the ability of an idea to provide insight into mathematics, whether by unifying disparate fields, introducing a new perspective on a single field, or providing a technique of proof which is either particularly simple, or captures the intuition or imagination as to why the result it proves is true. Gian-Carlo Rota distinguished between elegance of presentation and beauty of concept, saying that for example, some topics could be written about elegantly although the mathematical content is not beautiful, and some theorems or proofs are beautiful but may be written about inelegantly.
natural
Similar to "canonical" but more specific, this term makes reference to a description (almost exclusively in the context of transformations) which holds independently of any choices. Though long used informally, this term has found a formal definition in category theory.
pathological
An object behaves pathologically if it fails to conform to the generic behavior of such objects, fails to satisfy certain regularity properties (depending on context), or simply disobeys mathematical intuition. These can be and often are contradictory requirements. Sometimes the term is more pointed, referring to an object which is specifically and artificially exhibited as a counterexample to these properties.
rigor (rigour)
Mathematics strives to establish its results using indisputable logic rather than informal descriptive argument. Rigor is the use of such logic in a proof.
well-behaved
An object is well-behaved (in contrast with being pathological) if it does satisfy the prevailing regularity properties, or sometimes if it conforms to intuition (but intuition often suggests the opposite behavior as well).
Descriptive informalities
Although ultimately every mathematical argument must meet a high standard of precision, mathematicians use descriptive but informal statements to discuss recurring themes or concepts with unwieldy formal statements. Note that many of the terms are completely rigorous in context.
almost all
A shorthand term for "all except for a set of measure zero", when there is a measure to speak of. For example, "almost all real numbers are transcendental" because the algebraic numbers form a countable set of measure zero. One can also speak of "almost all" integers having a property to mean "all but finitely many", despite the integers not admitting a measure for which this agrees with the previous usage. For example, "almost all prime numbers are odd". There is a more complicated meaning for integers as well, discussed in the main article. Finally, this term is sometimes used synonymously with generic, below.
arbitrarily large, arbitrarily small, arbitrarily close
Notions which arise mostly in the context of limits, referring to the recurrence of a phenomenon as the limit is approached. A statement such as that predicate P is satisfied by arbitrarily large values, can be expressed in more formal notation by ∀x : ∃y ≥ x : P(y). See also frequently.
arbitrary
A shorthand for the universal quantifier. An arbitrary choice is one which is made unrestrictedly, or alternatively, a statement holds of an arbitrary element of a set if it holds of any element of that set.
eventually
In the context of limits, this is shorthand for for sufficiently large arguments; the relevant argument(s) are implicit in the context. As an example, one could say that "The function log(log(x)) eventually becomes larger than 100"; in this context, "eventually" means "for sufficiently large x".
factor through
A term in category
theory referring to composition of functions.
If we have three objects A, B, C,
a map 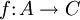 which is written as a composition
which is written as a composition 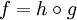 with
with  , ,
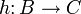 is said to factor through any (and all) of
B, g, and
h.
finite
Next to the usual meaning of "not infinite", in another more restrictive meaning that one may encounter, a value being said to be "finite" also excludes infinitesimal values and the value 0. For example, if the variance of a random variable is said to be finite, this implies it is a positive real number.
frequently
In the context of limits, this is shorthand for arbitrarily large and its relatives; as with eventually, the intended variant is implicit. As an example, one could say that "The function sin(x) is frequently zero", where "frequently" means "for arbitrarily large x".
generic
This term has similar connotations as almost all but is used particularly for concepts outside the purview of measure theory. A property holds "generically" on a set if the set satisfies some (context-dependent) notion of density, or perhaps if its complement satisfies some (context-dependent) notion of smallness. For example, a property which holds on a dense GΔ (intersection of countably many open sets) is said to hold generically. In algebraic geometry, one says that a property of points on an algebraic variety that holds on a dense Zariski open set is true generically; however, it is usually not said that a property which holds merely on a dense set (which is not Zariski open) is generic in this situation.
in general
In a descriptive context, this phrase introduces a simple characterization of a broad class of objects, with an eye towards identifying a unifying principle. Concisely, this term introduces an "elegant" description which holds for "arbitrary" objects "modulo" "pathology".
left-hand side, right-hand side (LHS, RHS)
Most often, these refer simply to the left-hand or the right-hand side of an equation; for example, x = y + 1 has x on the LHS and y +1 on the RHS. Occasionally, these are used in the sense of lvalue and rvalue: an RHS is primitive, and an LHS is derivative.
proper
If, for some notion of substructure, objects are substructures of themselves (that is, the relationship is reflexive), then the qualification proper requires the objects to be different. For example, a proper subset of a set S is a subset of S that is different from S, and a proper divisor of a number n is a divisor of n that is different from n. This overloaded word is also non-jargon for a proper morphism.
resp.
(Respectively) A convention to shorten parallel expositions. "A (resp. B) [has some relationship to] X (resp. Y)" means that A [has some relationship to] X and also that B [has (the same) relationship to] Y.
sharp
Often, a mathematical theorem will establish constraints on the behavior of some object; for example, a function will be shown to have an upper or lower bound. The constraint is sharp if it cannot be made more restrictive without failing in some cases.
smooth
Smoothness is a concept which mathematics has endowed with many meanings, from simple differentiability to infinite differentiability to analyticity, and still others which are more complicated. Each such usage attempts to invoke the physically intuitive notion of smoothness.
strong, stronger
A theorem is said to be strong if it deduces restrictive results from general hypotheses. One celebrated example is Donaldson's theorem, which puts tight restraints on what would otherwise appear to be a large class of manifolds. This (informal) usage reflects the opinion of the mathematical community: not only should such a theorem be strong in the descriptive sense (below) but it should also be definitive in its area. A theorem, result, or condition is further called stronger than another one if a proof of the second can be easily obtained from the first. An example is the sequence of theorems: Fermat's little theorem, Euler's theorem, Lagrange's theorem, each of which is stronger than the last; another is that a sharp upper bound (see above) is a stronger result than a non-sharp one. Finally, the adjective strong or the adverb strongly may be added to a mathematical notion to indicate a related stronger notion; for example, a strong antichain is an antichain satisfying certain additional conditions, and likewise a strongly regular graph is a regular graph meeting stronger conditions. When used in this way, the stronger notion (such as "strong antichain") is a technical term with a precisely defined meaning; the nature of the extra conditions cannot be derived from the definition of the weaker notion (such as "antichain").
sufficiently large, suitably small, sufficiently close
In the context of limits, these terms refer to some (unspecified, even unknown) point at which a phenomenon prevails as the limit is approached. A statement such as that predicate P holds for sufficiently large values, can be expressed in more formal notation by ∃x : ∀y ≥ x : P(y). See also eventually.
upstairs, downstairs
A descriptive term referring to notation in which two objects are written one above the other; the upper one is upstairs and the lower, downstairs. For example, in a fiber bundle, the total space is often said to be upstairs, with the base space downstairs. In a fraction, the numerator is occasionally referred to as upstairs and the denominator downstairs, as in "bringing a term upstairs".
up to, modulo, mod out by
An extension to mathematical discourse of the notions of modular arithmetic. A statement is true up to a condition if the establishment of that condition is the only impediment to the truth of the statement.
vanish
To assume the value 0. For example, "The function sin(x) vanishes for those values of x that are integral multiples of π." This can also apply to limits: see Vanish at infinity.
weak, weaker
The converse of strong.
is said to factor through any (and all) of
B, g, and
h.
finite
Next to the usual meaning of "not infinite", in another more restrictive meaning that one may encounter, a value being said to be "finite" also excludes infinitesimal values and the value 0. For example, if the variance of a random variable is said to be finite, this implies it is a positive real number.
frequently
In the context of limits, this is shorthand for arbitrarily large and its relatives; as with eventually, the intended variant is implicit. As an example, one could say that "The function sin(x) is frequently zero", where "frequently" means "for arbitrarily large x".
generic
This term has similar connotations as almost all but is used particularly for concepts outside the purview of measure theory. A property holds "generically" on a set if the set satisfies some (context-dependent) notion of density, or perhaps if its complement satisfies some (context-dependent) notion of smallness. For example, a property which holds on a dense GΔ (intersection of countably many open sets) is said to hold generically. In algebraic geometry, one says that a property of points on an algebraic variety that holds on a dense Zariski open set is true generically; however, it is usually not said that a property which holds merely on a dense set (which is not Zariski open) is generic in this situation.
in general
In a descriptive context, this phrase introduces a simple characterization of a broad class of objects, with an eye towards identifying a unifying principle. Concisely, this term introduces an "elegant" description which holds for "arbitrary" objects "modulo" "pathology".
left-hand side, right-hand side (LHS, RHS)
Most often, these refer simply to the left-hand or the right-hand side of an equation; for example, x = y + 1 has x on the LHS and y +1 on the RHS. Occasionally, these are used in the sense of lvalue and rvalue: an RHS is primitive, and an LHS is derivative.
proper
If, for some notion of substructure, objects are substructures of themselves (that is, the relationship is reflexive), then the qualification proper requires the objects to be different. For example, a proper subset of a set S is a subset of S that is different from S, and a proper divisor of a number n is a divisor of n that is different from n. This overloaded word is also non-jargon for a proper morphism.
resp.
(Respectively) A convention to shorten parallel expositions. "A (resp. B) [has some relationship to] X (resp. Y)" means that A [has some relationship to] X and also that B [has (the same) relationship to] Y.
sharp
Often, a mathematical theorem will establish constraints on the behavior of some object; for example, a function will be shown to have an upper or lower bound. The constraint is sharp if it cannot be made more restrictive without failing in some cases.
smooth
Smoothness is a concept which mathematics has endowed with many meanings, from simple differentiability to infinite differentiability to analyticity, and still others which are more complicated. Each such usage attempts to invoke the physically intuitive notion of smoothness.
strong, stronger
A theorem is said to be strong if it deduces restrictive results from general hypotheses. One celebrated example is Donaldson's theorem, which puts tight restraints on what would otherwise appear to be a large class of manifolds. This (informal) usage reflects the opinion of the mathematical community: not only should such a theorem be strong in the descriptive sense (below) but it should also be definitive in its area. A theorem, result, or condition is further called stronger than another one if a proof of the second can be easily obtained from the first. An example is the sequence of theorems: Fermat's little theorem, Euler's theorem, Lagrange's theorem, each of which is stronger than the last; another is that a sharp upper bound (see above) is a stronger result than a non-sharp one. Finally, the adjective strong or the adverb strongly may be added to a mathematical notion to indicate a related stronger notion; for example, a strong antichain is an antichain satisfying certain additional conditions, and likewise a strongly regular graph is a regular graph meeting stronger conditions. When used in this way, the stronger notion (such as "strong antichain") is a technical term with a precisely defined meaning; the nature of the extra conditions cannot be derived from the definition of the weaker notion (such as "antichain").
sufficiently large, suitably small, sufficiently close
In the context of limits, these terms refer to some (unspecified, even unknown) point at which a phenomenon prevails as the limit is approached. A statement such as that predicate P holds for sufficiently large values, can be expressed in more formal notation by ∃x : ∀y ≥ x : P(y). See also eventually.
upstairs, downstairs
A descriptive term referring to notation in which two objects are written one above the other; the upper one is upstairs and the lower, downstairs. For example, in a fiber bundle, the total space is often said to be upstairs, with the base space downstairs. In a fraction, the numerator is occasionally referred to as upstairs and the denominator downstairs, as in "bringing a term upstairs".
up to, modulo, mod out by
An extension to mathematical discourse of the notions of modular arithmetic. A statement is true up to a condition if the establishment of that condition is the only impediment to the truth of the statement.
vanish
To assume the value 0. For example, "The function sin(x) vanishes for those values of x that are integral multiples of π." This can also apply to limits: see Vanish at infinity.
weak, weaker
The converse of strong.
Proofs and rigorous proof techniques
The formal language of proof draws repeatedly from a small pool of ideas, many of which are invoked through various lexical shorthands in practice.
aliter
An obsolescent term which refers to an alternative method of proof.
diagram chase[1]
Given a commutative diagram of objects and morphisms between them, if one wishes to prove some property of the morphisms (such as injectivity) which can be stated in terms of elements, then the proof can proceed by tracing the path of elements of various objects around the diagram as successive morphisms are applied to it. That is, one chases elements around the diagram, or does a diagram chase.
for all sufficiently nice X
For all X which satisfy a set of conditions to be specified later. When working out a theorem, the use of this expression in the statement of the theorem indicates that the conditions involved may be not yet known to the speaker, and that the intent is to collect the conditions that will be found to be needed in order for the proof of the theorem to go through.
if and only if (iff)
An abbreviation for logical equivalence of statements.
in general
In the context of proofs, this phrase is often seen in induction arguments when passing from the base case to the "induction step", and similarly, in the definition of sequences whose first few terms are exhibited as examples of the formula giving every term of the sequence.
necessary and sufficient
A minor variant on "if and only if"; necessary means "only if" and sufficient means '"if". For example, "For a field K to be algebraically closed it is necessary and sufficient that it have no finite field extensions" means "K is algebraically closed if and only if it has no finite extensions". Often used in lists, as in "The following conditions are necessary and sufficient for a field to be algebraically closed...".
need to show (NTS), required to prove (RTP), wish to show, want to show (WTS)
Proofs sometimes proceed by enumerating several conditions whose satisfaction will together imply the desired theorem; thus, one needs to show just these statements.
one and only one
An especially precise existence statement; the object exists, and furthermore, no other such object exists.
by way of contradiction (BWOC), or "for, if not, ..."
The rhetorical prelude to a proof by contradiction, preceding the negation of the statement to be proved.
Q.E.D.
(Quod erat demonstrandum): A Latin abbreviation historically placed at the end of proofs, but less common currently.
the following are equivalent (TFAE)
A particular definition is not always the most convenient for certain applications; often one proves theorems stating equivalent rephrasings of the definition.
transport of structure
It is often the case that two objects are shown to be equivalent in some way, and that one of them is endowed with additional structure. Using the equivalence, we may define such a structure on the second object as well, via transport of structure. For example, any two vector spaces of the same dimension are isomorphic; if one of them is given an inner product and if we fix a particular isomorphism, then we may define an inner product on the other space by factoring through the isomorphism.
without (any) loss of generality (WLOG, WOLOG, WALOG), we may assume (WMA), it may be assumed that (WOLOGIMBAT)
Sometimes a proposition can be more easily proved with additional assumptions on the objects it concerns. If the proposition as stated follows from this modified one with a simple and minimal explanation (for example, if the remaining special cases are identical but for notation), then the modified assumptions are introduced with this phrase and the altered proposition is proved.
Informal proof techniques
Some terms are techniques for the avoidance of rigorous proof, though are not logical fallacies. They suggest the content of a correct proof without supplying it.
- back-of-the-envelope calculation
- An informal computation omitting much rigor without sacrificing correctness. Often this computation is "proof of concept" and treats only an accessible special case.
- by inspection
- A rhetorical shortcut made by authors who invite the reader to verify, at a glance, the correctness of a proposed expression or deduction.
- clearly, can be easily shown
- A term which shortcuts around calculation the mathematician perceives to be tedious or routine, accessible to any member of the audience with the necessary expertise in the field; Laplace used obvious.
- handwaving
- A non-technique of proof mostly employed in lectures, where formal argument is not strictly necessary. It proceeds by omission of details or even significant ingredients, and is merely a plausibility argument.
- in general
- In a context not requiring rigor, this phrase often appears as a labor-saving device when the technical details of a complete argument would outweigh the conceptual benefits. The author gives a proof in a simple enough case that the computations are reasonable, and then indicates that "in general" the proof is similar.
- morally true
- Used to indicate that the speaker believes a statement should be true, given their mathematical experience, even though a proof has not yet been put forward. As a variation, the statement may in fact be false, but instead provide a slogan for or illustration of a correct principle. Hasse's local-global principle is a particularly influential example of this.
- trivial
- Similar to clearly. A concept is trivial if it holds by definition, is immediately corollary to a known statement, or is a simple special case of a more general concept.
Footnotes
- ^ Numerous examples can be found in (Mac Lane 1998), for example on p. 100.
References
- Monastyrsky, Michael (2001), "Some Trends in Modern Mathematics and the Fields Medal", Can. Math. Soc. Notes 33 (2 and 3), http://www.fields.utoronto.ca/...Monastyrsky.pdf
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1997), "The PNAS way back then", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 5983–5985, http://www.pnas.org/cgi/reprint/94/12/5983.pdf
- Eilenberg, Samuel; Mac Lane, Saunders (1942), "Natural Isomorphisms in Group Theory", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 28: 537–543
- Poincare, Henri (1913), Halsted, Bruce, ed., The Foundations of Science, The Science Press, p. 435, http://books.google.com/...M1
- Pinto, J. Sousa (2004), Hoskins, R.F., ed., Infinitesimal methods for mathematical analysis, Horwood Publishing, p. 246, http://books.google.com/...M1
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1998), Categories for the Working Mathematician, Springer
- Shafarevich, Igor (1991), Kandall, G.A., ed., Algebraic Geometry, IV, Springer
- Rota, Gian-Carlo (1977), "The phenomenology of mathematical beauty", Synthese 111 (2): 171–182, ISSN 0039-7857
- Jackson, Allyn (2004), "Comme Appelé du Néant — As If Summoned from the Void: The Life of Alexandre Grothendieck", AMS Notices 51 (9,10) (Parts I and II)
- Fundamentals of Mathematics, Global Media, ISBN 8189940570, http://books.google.com/...xhjo
- Wiedijk, Freek, ed. (2006), The Seventeen Provers of the World, Birkhäuser, ISBN 3540307044
Published - March 2009
This
glossary is available under the terms
of the GNU Free Documentation
Find free glossaries at TranslationDirectory.com
Find free dictionaries at TranslationDirectory.com
Subscribe to free TranslationDirectory.com newsletter
Need more translation jobs from translation agencies? Click here!
Translation agencies are welcome to register here - Free!
Freelance translators are welcome to register here - Free!
Submit your glossary or dictionary for publishing at TranslationDirectory.com
|